December 2024
2MR Report
Author: Eymeric Chauchat
Version: V1.0 (11 Nov 2024)
Precedent report - Next report
Goal and motivation of the report
The present report is the first 2MR report. In this sense, it will summarize the research goal about xl-sindy. A past overview of the research can be accessed through the May 2023 Report. After a short introduction and this presentation, the work through the last months will be presented.
Introduction
In the introduction, the different chapters that are going to follow will be presented. The importance of each section concerning the actual xl-sindy research will be stated.
- Research goal : This section gives a summary of the xl-sindy research. Even though the following presentation will be updated from the May 2023 Report, the core objectives remain unchanged. An overview of less important goals will also be listed (called Life sub-goals).
- Life sub goals: this section is supplementary, in the sense that it won’t be closely related with the main research but will give a technical overview of the tool used to conduct research like the one presented.
- Python Xl-Sindy Library : The process of creating a Python library will be explained.
- Reinforcement learning basics : This part will explain the theoretical fundamentals of reinforcement and give the link that this will have on the xl-sindy research.
Research goal
An updated overview of the research will be presented through goals and sub-goals.
The main goal is to develop a complete control framework using Euler Lagrange SINDy. Some sub-objectives can be listed subsequently:
- Achieve a complete interpretable control scheme while being data learned
- Compare our framework with RL-SINDy
- Run it on a real robot
Sub-goal
A list of research sub-goals will be given with some reason for their selection. Sub-goals can possess two natures: they can be closely research-related ( R ) and some others can be more related to tools and ways to manage research ( L ). The life-related sub-goal can be seen as an explanation for the extra time passed on research leading to a not-direct result.
( R ) Xl-sindy Python library
Initially conceived as a concept, the XL-SINDy Python library has now been developed into a functional reality. In order to get a clear code base only concerning the Xl-Sindy algorithm, it was important to correctly organize this code into a library.
The code was already cleaner after a second rewrite (May 2023#code-rebuild) but even with this effort, it became complex again to work with it after some time without using it.
This sub-goal required moderate effort due to the groundwork already completed.
( R ) Get knowledge about Deep Reinforcement Learning
Around June, a first try with Deep Reinforcement Learning was done. Although some experiments yielded positive results, the majority failed due to unknown factors. These challenges necessitated that more knowledge about Deep Reinforcement Learning needed to be acquired.
( L ) Become git efficient
Becoming efficient with git was deemed necessary to streamline the integration and testing of xl-Sindy algorithms and of the library.
( L ) Get notes management software.
The complexity of the project evolving rapidly with the addition of multiple layers of algorithms and the increasing size of the framework, a solution for taking notes has been needed. Extensive evaluations of note-taking tools demonstrated the need for a systematic approach.
Storing the valuable resources only through the markdown in the different github repository became a bottleneck for efficiency.
( L ) Learn how to write in an impersonal scientific tone.
Preparing for a February publication necessitated learning how to write in a scientific and impersonal tone. Even though a continuous effort for writing in this manner is given, improvement is slow, and the whole process requires much more time than writing in a personified manner.
A particular attention has been given during the writing of the tutorial for the creation of a Python library.
Conference goal
The goal to publish for IROS 25 in China has been set. The following part could be sufficient material for the paper:
- Compare Xl-Sindy with RL-Sindy on a Lagrangian-compatible system
- Present the py-xl-sindy Python library
- (Optional) Show result on a true robot
Life Sub goals
The different tool used in the past month to enhance research workflow will be presented in the next section.
Zotero Referencing Software
Zotero has been adopted as a referencing tool to enhance research efficiency, providing streamlined citation management and annotation capabilities. Zotero can keep track of every read paper. Zotero is entirely open source software that retrieves citing data from a high number of journal publishers. The software composes a library of documents that can be efficiently linked through Bibtex or any other citing format. The ease of use to add paper to the library through a Firefox addon, in addition to the simplicity to annotate and share paper, has turned Zotero into an unvaluable tool.
Joplin note-taking app
This app enables a fast and practical take of notes; everything is taken in markdown. The layered structure of the notebook enables a high granularity in the sorting of the note.
In the end, no other text editor is used anymore. Every command, short tutorial, or thought can be taken through the Joplin app on a phone or computer.
Joplin, an open-source note-taking application, supports markdown-based notes and can be synchronized using a self-hosted server.
An active community maintains the code and creates a lot of different useful plugins. Key plugins that enhanced the functionality of the Joplin app are described below.
Static github.io website
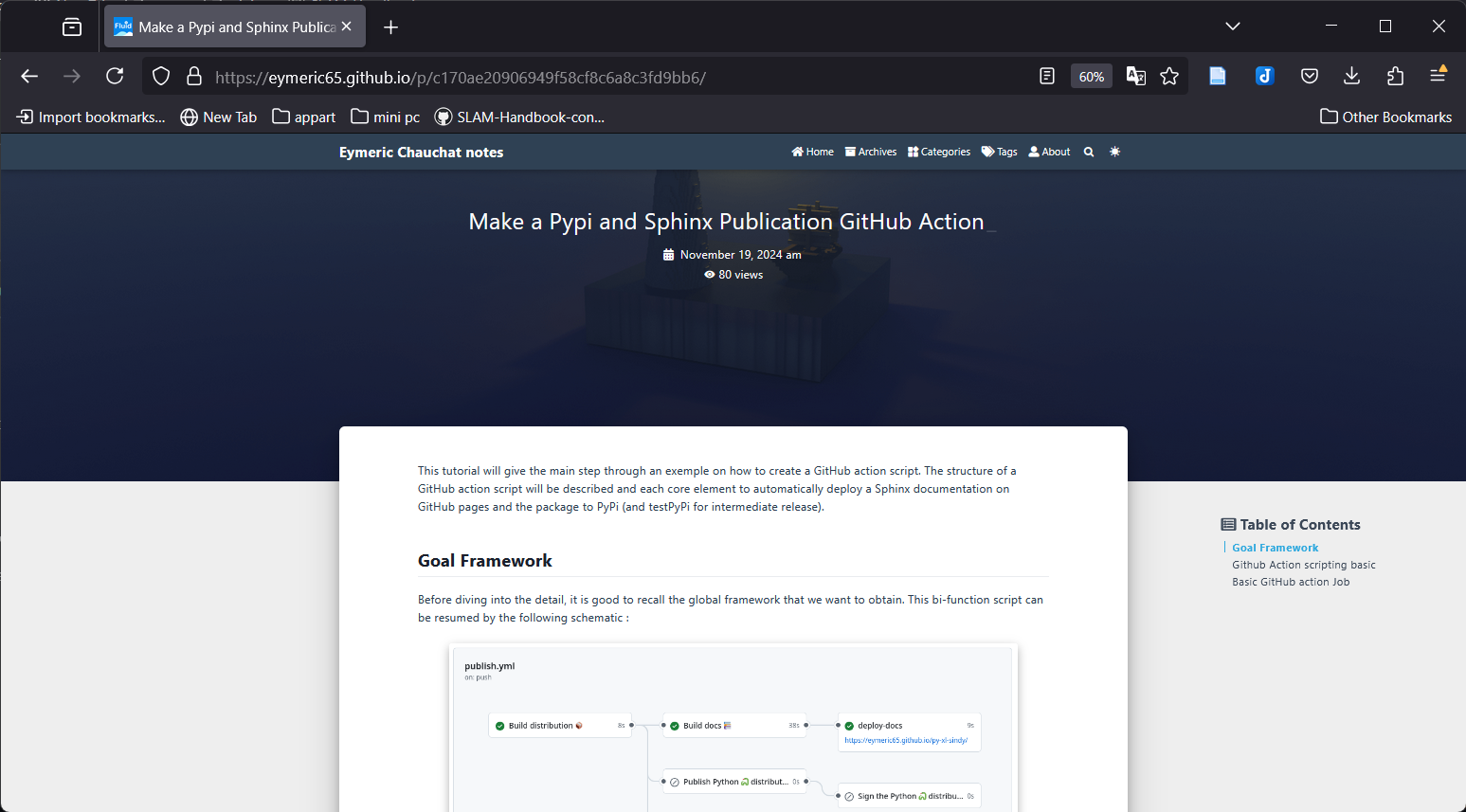
The main plugin for this kind of report is the ability to use Joplin as a content management software for static pages on websites (like blogs). In an automated manner, every note tagged blog can be synchronized and sent to a repository that will generate through github pages a static website. This tool has proven highly effective for sharing devlogs or tutorials with other people.
Graphe visualization and UI improvement
The main advantage of taking notes instead of wiki engines is the possibility to create floating notes (referenced nowhere). This advantage is mitigated by the fact that floating notes can be lost in the quantity (and only retrieved by searching). Graph visualization effectively supports tracking and organizing floating notes.

Referencing from bibTex
Joplin can be linked through a Bibtex file in order to quickly cite the author.
The Bibtex is automatically updated by Zotero closing the loop between the two software.
Get better at git
A good understanding of the git software is needed in order to maintain a Python library. This knowledge has been acquired at the same time of formatting the library. A precise overview can be read there: Creating a Python library#summary-of-git-strategy
Python Xl-Sindy Library
In order to be able to compare efficiently xl-Sindy with other Sindy algorithms, it was needed to have an abstract way to launch simulation using xl-Sindy. One of the easiest ways was to compile xl-Sindy as a Python library.
A good way to keep all the knowledge inside xl-Sindy is to develop a well-documented library through extensive documentation. The details of all the processes can be found here : Creating a Python library .
The maintainer repository can be found on git py-xl-sindy and the actual binary is automatically pushed to PyPi at each release py-xl-sindy
Reinforcement learning learning
The quest for knowledge for reinforcement learning has started by try and error using Reinforcement Learning algorithm. Excempted of much detail, a quick overview of the state of the research concerning reinforcement learning will be given.
Reinforcement learning framework
During the different tests about reinforcement learning, two main frameworks have been tried:
- Rlib
- CleanRL
Rlib @liangRLlibAbstractionsDistributed2018
RLib has been used at first to launch the first Reinforcement learning experiment. The use of GYMnasium as the environment maker increases by a lot the difficulty of use of RLib. The high level of abstraction given through Rlib can be seen as one of the major difficulties of this software. However, since RLib is used by the RL-Sindy team @zolmanSINDyRLInterpretableEfficient2024 A more in-depth review of RLib needs to be done in the following month.
CleanRL @huangCleanRLHighqualitySinglefile2021
CleanRL is a python library that focuses on the implementation of state-of-the-art algorithm in one file.
In order to deeply understand the underline mechanics inside a Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithm, CleanRL becomes handy. Due to the extreme control given by CleanRL, the goal is to be able to perform comparisons of the SINDy framework through CleanRL.
In order to install CleanRL (and poetry lib manager on the laboratory server) Some resources are provided here: Clean RL Installation
Reinforcement Learning theory
A vast set of papers about Reinforcement Learning made reference to a book @suttonReinforcementLearningIntroduction. A personnal reading note can be found here Reinforcement Learning An Introduction book (really informal). The book has provided foundational insights into reinforcement learning.
It covers topics from the beginning of reinforcement learning. With exploration of finite action domain and solution to one state problem until the more complex policy algorithm (that leads to an algorithm like PPO).
A concise summary of reinforcement learning fundamentals is provided in the next paragraph. Since the book has been studied only until the Tabular method, an overview of this part only will be given in this report.
- Greedy, $\epsilon$-greedy, …
Reinforcement learning has in it heart the concept of learning. Learning means that some times you need to make mistakes, whether they are short-term mistakes (something that can be seen as a mistake but in fact, in the long run, enable a better outcome) or just mistakes that pave the way for the optimal outcome. In reinforcement learning, taking the action that maximizes the known outcome is called taking a greedy action. Always taking a greedy action is a good way to maximize the known outcome (by definition, maximizing it) but it is really bad to be greedy when the action domain is needed to be explored. That’s why there are a lot of ways to choose action. For example, the $\epsilon$-greedy method states that with a probability of $\epsilon$ a total random action should be chosen instead of taking a greedy one. - Dynamic Programming method :
This is the base of every Reinforcement learning, a true tabular method. The goal of Dynamic Programming is to optimally solve sub-problems in order to grasp the solution of the whole problem. Usually Dynamic programming method will solve every problem possible before finding the solution to our specific problem (choosing every solution path to be certain that our problem has the optimal solution). - Monte Carlo method :
Monte Carlo method is the first statistical method that appears in the book. The goal is simple: take random (but in a clever way) action in order to, on average, converge to the optimal solution. This method, unlike Dynamic Programming doesn’t usually need to solve the whole problem in order to get the solution of ours. The statistical nature of monte carlo enable the algorithm to explore local solutions in order to find the global minimum (Soap bubble height algorithm is an intuitive proof for it)
References
- Zolman, N., Fasel, U., Kutz, J. N. & Brunton, S. L. SINDy-RL: Interpretable and Efficient Model-Based Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv, 2024).
- Huang, S., Dossa, R. F. J., Ye, C. & Braga, J. CleanRL: High-Quality Single-File Implementations of Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. (arXiv, 2021). doi:10.48550/arXiv.2111.08819.
- Liang, E. et al. RLlib: Abstractions for Distributed Reinforcement Learning. (arXiv, 2018). doi:10.48550/arXiv.1712.09381.
- Sutton, R. S. & Barto, A. G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction.